
Telephone
025-52791167,52791168
13390905858
13390905858
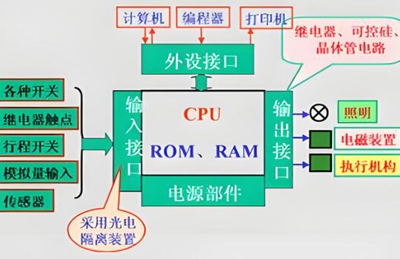
Full analysis of input and output interfaces for PLC programmable controllers
Input interface: Sensing the tentacles of the outside world
The input interface is like the sensitive “antennae” of a PLC, responsible for receiving signals from external devices. Common external devices include buttons, sensors, switches, etc. These devices generate a wide variety of signal types, including switch signals (with only on and off states) and analog signals (such as continuously changing voltage, current, etc.).
Taking industrial automation production lines as an example, various sensors monitor the real-time operation status of equipment and transmit the collected signals to the input interface of PLC. The input interface of PLC will process and convert these signals. Taking switch input as an example, when an external button is pressed, the signal enters the internal circuit of the PLC through the input interface. During this process, the input interface will perform photoelectric isolation operations, which can effectively block external circuit interference signals from entering the PLC and avoid affecting its normal operation, just like putting a solid layer of “protective armor” on the PLC. For analog input, the input interface will convert the analog signal into a digital signal, because the PLC uses digital signals for operation and processing, just like accurately translating different languages into digital languages that the PLC can “understand”.
Output interface: Bridge for executing control
The output interface is a critical channel for PLC to send control signals to external devices. With the help of output interfaces, PLC can control devices such as relays, contactors, solenoid valves, etc. The output interface is also divided into switch output and analog output.
When outputting switch values, the PLC controls the circuit on/off of the output interface based on the calculation results of the program, thereby controlling the working status of external devices. For example, when controlling the start and stop of a motor, when the output interface of the PLC is turned on and the relay is closed, the motor starts to run; When the output interface is disconnected, the relay is released and the motor immediately stops. Analog output is used to output continuously changing signals to control devices that require precise adjustment, such as by outputting different voltage or current signals to accurately adjust the opening of valves, thereby achieving precise control of flow rate.

telephone:025-52791167,52791168
Fax:025-52791169
Phone :13390905858
mailbox:njxj888@163.com skype:yluedq
Address:Jiangning Shuanglong Avenue No.1222 Nanjing, Jiangsu. China P.O. 211100