
Telephone
025-52791167,52791168
13390905858
13390905858
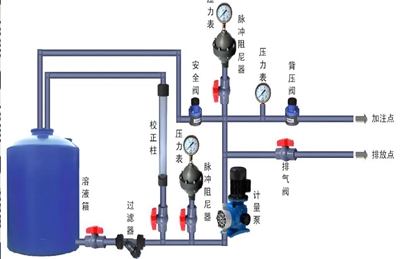
Common faults and solutions of metering pumps
Metering pumps play an important role in industrial production, and their precise metering and stable conveying performance are indispensable for the smooth progress of many processes. However, in the long-term use process, various faults may occur in the metering pump. Below, we will explore some common faults and solutions.
1、 The pump is not running
Reason for malfunction
Power supply issues: The motor cannot receive power supply due to power failure, blown fuses, loose or damaged power cords, etc.
Motor malfunction: Short circuit, open circuit, grounding of motor winding, or damage to motor bearings, causing the motor to malfunction.
Control circuit failure: Controller failure, relay damage, poor circuit contact, etc., affecting the transmission of motor control signals.
Mechanical jamming: Internal components of the pump, such as impellers and pistons, are jammed by debris, or the gap between the pump shaft and bearings is too small, resulting in mechanical jamming.
solution
Check the power supply, ensure it is connected, replace the blown fuse, repair or replace the damaged power cord.
Check the motor, use a multimeter or other tools to measure the resistance value of the motor winding, and determine if there are any short circuits, open circuits, or other issues. If necessary, replace the motor or repair the motor winding. At the same time, check the motor bearings and replace them promptly if they are damaged.
Check the control circuit, repair or replace faulty controllers, relays, and other components to ensure good circuit connections.
Disassemble the pump body, clean up debris, check the installation of components, adjust the gap between the pump shaft and bearings, and ensure that the mechanical components can operate normally.
2、 Inaccurate measurement
Reason for malfunction
Adjustment mechanism failure: The adjustment mechanism of the metering pump, such as the adjustment handwheel and screw, has malfunctioned, resulting in inaccurate flow regulation.
Unstable pump speed: Motor speed fluctuations, loose or slipping transmission belts, etc. can cause unstable pump speed, thereby affecting measurement accuracy.
Changes in liquid viscosity: Changes in liquid viscosity can affect the flow characteristics of the pump, leading to inaccurate measurement.
Pump leakage: Poor sealing of the pump head, damaged diaphragm, and other leakage issues can cause the actual output flow rate to be lower than the set flow rate.
solution
Check the adjustment mechanism, repair or replace faulty components, and ensure that the adjustment handwheel, adjustment screw, etc. can adjust the flow rate normally.
Check the motor speed, adjust the operating parameters of the motor to ensure stable speed. At the same time, check the tension of the transmission belt. If there is any looseness or slippage, adjust or replace the belt in a timely manner.
Adjust the working parameters of the pump or select the appropriate pump type based on changes in liquid viscosity.
Check the sealing condition of the pump, replace damaged diaphragms and seals, and ensure good sealing of the pump head.
3、 Pump body overheating
Reason for malfunction
Poor lubrication: Insufficient lubrication of pump bearings, gears, and other components can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and overheating of the pump body.
Overload operation: If the working pressure of the pump is too high, the flow rate is too large, or the viscosity of the conveyed liquid exceeds the design range, it will cause the pump to overload and generate excessive heat.
Poor heat dissipation: Poor ventilation conditions around the pump body or blocked heat sinks can affect the heat dissipation effect of the pump body, leading to an increase in temperature.
solution
Check the lubrication system, add or replace lubricating oil, and ensure that all components are adequately lubricated.
Check the working parameters of the pump, adjust the working pressure and flow rate to operate within the design range. At the same time, check the viscosity of the conveyed liquid and take appropriate measures to handle it if necessary.
Improve the ventilation conditions around the pump body, clean up debris on the heat sink, and ensure good heat dissipation.
By analyzing and solving common faults in metering pumps, equipment failures can be detected and eliminated in a timely manner, ensuring the normal operation of metering pumps and improving production efficiency and product quality.

telephone:025-52791167,52791168
Fax:025-52791169
Phone :13390905858
mailbox:njxj888@163.com skype:yluedq
Address:Jiangning Shuanglong Avenue No.1222 Nanjing, Jiangsu. China P.O. 211100