The influence of
power module wiring method on output power
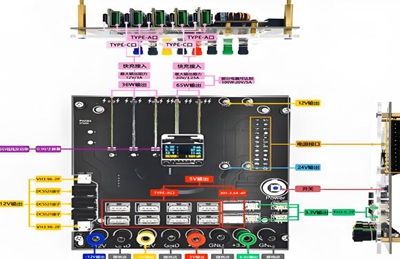
The wiring method of the power module has a crucial impact on the output power of electronic devices during operation. The correct wiring method can ensure stable and efficient power output of the power module, meeting the operational requirements of the equipment; The wrong wiring method may lead to a decrease in output power, equipment failure, and even damage to the power module.
For a single power module, the wiring of the input voltage must be ensured to be within its rated range. If the input voltage is too low, the output value of a constant voltage or wide voltage power module will also be correspondingly low. When the input voltage is too low, the module may not work and there may be no output voltage. In addition, attention should also be paid to the connection between the output end and the load. If the impedance of the wiring is too high, such as too long or too narrow, or if there is poor contact between solder joints or oxidation corrosion of the circuit, it will increase the equivalent resistance, which will act as a voltage divider, causing the voltage at both ends of the load to be lower than the output voltage of the module, thereby affecting the output power.
The impact of wiring methods is more complex when multiple power modules are connected in parallel. When connecting in parallel, it is necessary to connect the positive and negative terminals of all power sources. However, it should be noted that the same model of power module must be used, and the length and diameter of the parallel connected cables should be consistent to ensure the stability of the power output voltage and current. Connecting wires of different lengths can increase impedance changes and voltage drops, leading to unstable output. At the same time, the output terminals of the power module should be connected to the load separately. If multiple power sources share a load, if one of the power sources fails, it may cause the output current of the shared load’s power source to be too high, damaging the load.
Taking the
power module of the S7-1500 series PLC as an example, there are multiple combination configurations between its system power supply and CPU. When the system power is on the far left and there is a DC24V power supply on the power terminal of the CPU, the CPU and the system power supply will supply power to the module together through the backplane bus. The power supply on the backplane bus is the sum of the system power supply and the power of the CPU, which can connect more modules and increase the output power. When the system power supply is on the right side of the CPU, due to the reverse diode inside the system power supply, the power supply path from the CPU to the backplane bus is blocked, and all power on the module backplane bus is provided by the system power supply. At this time, the DC24V terminal of the CPU must be powered. This method can be used to expand the power supply when there are enough modules and the backplane bus power supply is insufficient.